What is Bipolar Disorder?
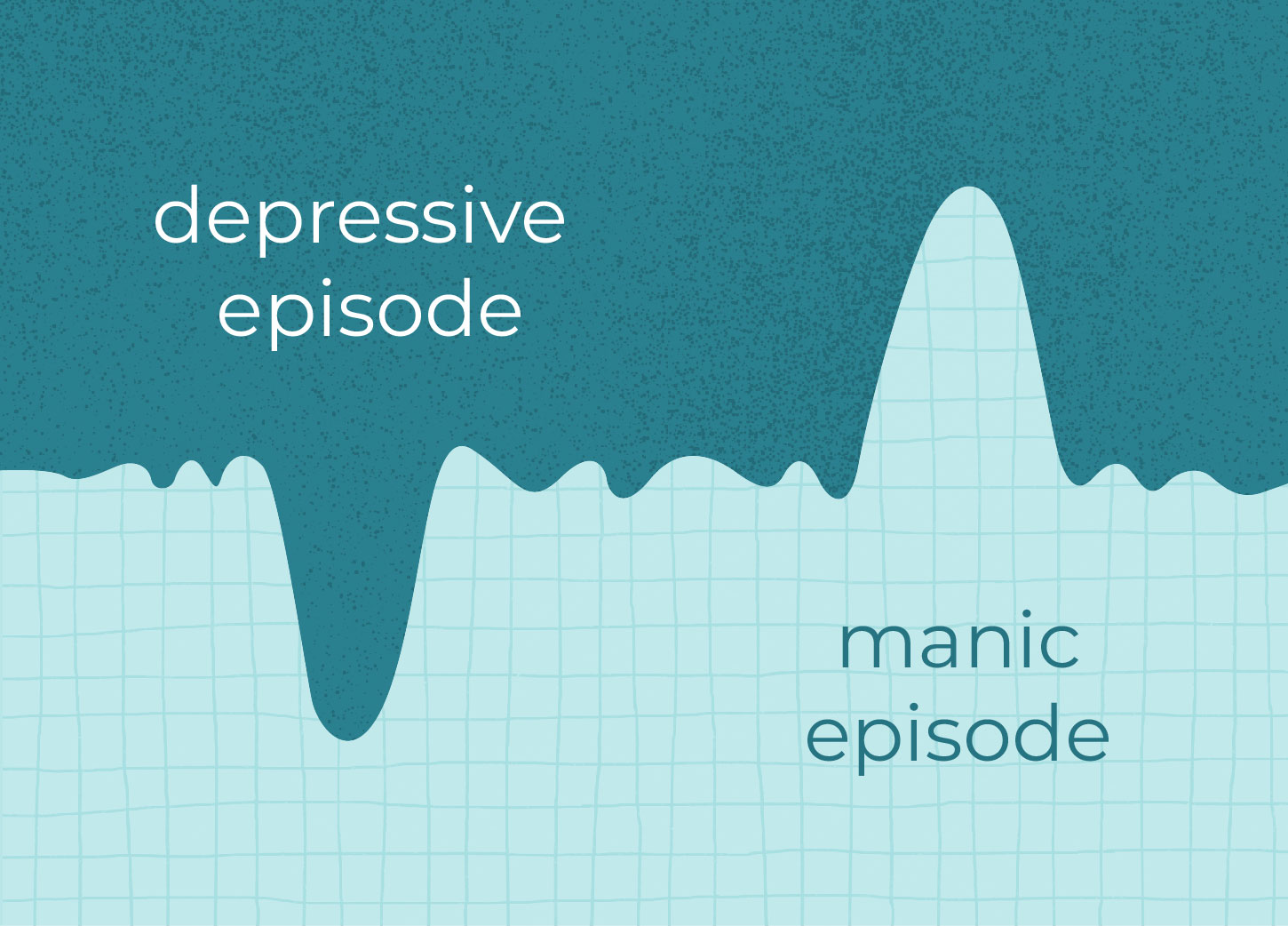
Bipolar Disorder, formerly known as manic depression, is a mental health condition characterised by extreme shifts in mood, energy levels, and activity levels. Individuals with bipolar disorder experience periods of intense highs, known as mania or hypomania, and periods of deep lows, known as depression. These mood swings can significantly impact daily life, relationships, and overall well-being.
Bipolar I Disorder
This type of bipolar disorder is defined by the occurrence of at least one manic episode, which may be preceded or followed by hypomanic or depressive episodes. Manic episodes are characterised by elevated mood, extreme energy, racing thoughts, impulsive behaviour, and a heightened sense of self-importance. These episodes can be severe and may require hospitalisation.
Bipolar II Disorder
Bipolar II disorder involves recurrent episodes of major depression and hypomania. Hypomania is a less severe form of mania, characterised by a distinct period of elevated mood, increased energy, and heightened creativity. While hypomania does not typically lead to severe impairment or hospitalisation, it can still disrupt daily life.
Cyclothymia
Cyclothymia is a milder form of bipolar disorder characterised by numerous periods of hypomanic symptoms and depressive symptoms that persist for at least two years. The symptoms are less severe than those of Bipolar I or II, but they can still interfere with daily function.